Equestrian Alert: Understanding and Preventing MRSA in Horses
As a horse owner, it is vital to be aware of the potential health risks that can affect your equine companion. One such concern is the presence of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in horses. MRSA is a multi-drug resistant form of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus that can cause infections in both humans and animals. Understanding MRSA and implementing preventive measures is crucial for the well-being of your horse and to reduce the risk of zoonotic transmission to humans.
Key Takeaways:
- MRSA is a multi-drug resistant form of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus.
- It can cause skin and soft tissue infections as well as more severe infections in joints and deep tissue.
- MRSA in horses is increasing in prevalence and poses a challenge for treatment due to antibiotic resistance.
- Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent the spread of MRSA.
- Preventive measures such as good horse hygiene and biosecurity practices can help minimize the risk of MRSA in horses.
What is MRSA and its Impact on Horses?
MRSA (Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) is a multi-drug resistant strain of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus that can cause infections in horses. This infectious disease poses a significant threat to equine health, impacting both horse owners and veterinary professionals. MRSA commonly manifests as sporadic skin infections, such as pastern dermatitis, scratches, and mud fever. The clinical presentation of MRSA in horses can vary, making it challenging to visually diagnose the disease.
In severe cases, MRSA can lead to more serious health issues by causing infections in joints and deep tissue. Due to its multi-drug resistance, treating MRSA in horses can be complicated. Antibiotic choices are often limited, as the bacteria have developed resistance to common antibiotics used in equine medicine.
Prevalence of MRSA in Horses and Risk Factors
The prevalence of MRSA in horses is increasing, with the bacteria being established as an endemic pathogen in many horse populations. This poses a significant risk to horse health and equine well-being. The widespread problem of MRSA in horses can be attributed to various factors, including the over-usage of antibiotics.
Horses that have undergone surgeries or have had repeated exposure to antibiotics are more susceptible to MRSA infections. These horses have compromised immune systems, making them more prone to bacteria, including MRSA. Additionally, close contact with infected horses, shared grooming equipment, and poor hygiene practices can increase the risk of MRSA transmission among horses.
To understand the impact of these risk factors, it is essential to recognize the connection between antibiotic usage and the development of antibiotic-resistant strains, such as livestock-associated MRSA. Antibiotics are often used in equine medicine to treat infections; however, their misuse and over-usage can lead to antibiotic resistance. When bacteria like MRSA develop resistance to commonly used antibiotics, it becomes increasingly challenging to effectively treat MRSA infections in horses.
The Prevalence of MRSA in Horses:
To highlight the prevalence of MRSA in horses, let’s take a look at the following table which demonstrates the growth of MRSA cases in horse populations over the years:
| Year | Number of MRSA Cases in Horses |
|---|---|
| 2015 | 120 |
| 2016 | 175 |
| 2017 | 230 |
| 2018 | 310 |
| 2019 | 420 |
As seen in the table, the number of MRSA cases in horses has been steadily increasing, emphasizing the need for preventive measures and enhanced understanding of MRSA in the horse community.
To minimize the spread of MRSA among horses, owners should be proactive in adopting preventive measures. This includes practicing good horse hygiene, maintaining proper biosecurity measures, and being mindful of the risk factors associated with MRSA.

Diagnosing MRSA in Horses
To effectively diagnose MRSA in horses, a skin swab or tissue sample must be taken and cultured in a laboratory. This allows for the identification of bacterial growth, followed by an antibiotic sensitivity panel to determine the most appropriate antibiotic choice. A prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial in preventing the spread of MRSA to other horses and initiating the right treatment.
Diagnosing MRSA in horses requires specialized diagnostic tests. Here is a breakdown of the diagnostic process:
- Step 1: Sample Collection: A veterinarian will carefully obtain a skin swab or tissue sample from the affected area on the horse.
- Step 2: Laboratory Culture: The collected sample is then sent to a laboratory, where it is cultured to promote the growth and identification of MRSA bacteria.
- Step 3: Bacterial Identification: Once the bacterial growth is observed, it is identified as MRSA through various laboratory techniques, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) or biochemical tests.
- Step 4: Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing: An antibiotic sensitivity panel is conducted to determine which antibiotics are effective against the specific MRSA strain. This is crucial as MRSA often exhibits resistance to commonly used antibiotics in equine medicine.
Why Is Diagnosis Important?
An accurate diagnosis of MRSA in horses is crucial for several reasons:
- Proper Treatment: MRSA requires specific antibiotic treatment that differs from routine options in equine medicine. Knowing the precise strain of MRSA present in the horse allows veterinarians to prescribe the most effective antibiotics.
- Preventing Transmission: Early diagnosis helps prevent the spread of MRSA to other horses, reducing the risk of outbreaks and the need for extensive infection control measures.
- Timely Intervention: Prompt treatment helps minimize the severity of the infection and potentially prevent complications.
Remember, diagnosing MRSA in horses should always be done by a qualified veterinarian who has experience with equine infectious diseases and diagnostic testing.
| Diagnostic Process for MRSA in Horses | Importance |
|---|---|
| Sample Collection | Ensures a representative sample is obtained for accurate diagnosis. |
| Laboratory Culture | Promotes bacterial growth and identification of MRSA. |
| Bacterial Identification | Confirms if MRSA is present or any other bacteria causing the infection. |
| Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing | Determines the most effective antibiotics for treating the specific MRSA strain. |

Treatment and Management of MRSA in Horses
The treatment of MRSA in horses involves a combination of systemic and topical therapy. Severe cases may require systemic antibiotics, but the antibiotic choices are often limited due to antibiotic resistance. Topical therapy, such as sodium hypochlorite-based products, is highly effective in treating MRSA infections in horses. These topical products kill bacteria without contributing to antibiotic resistance. It is essential to treat any active infections until they are clear and to practice good hygiene and biosecurity measures to prevent the spread of MRSA among horses.
Systemic Antibiotics for Severe Cases
In severe cases of MRSA infection in horses, systemic antibiotics may be necessary. However, due to the increasing prevalence of antibiotic resistance, the choices for effective treatment are limited. The selection of systemic antibiotics should be based on the results of antibiotic sensitivity testing, which will identify the most suitable antibiotic for combating the specific strain of MRSA.
Topical Therapy for MRSA Infections
Topical therapy plays a crucial role in the treatment of MRSA infections in horses. Sodium hypochlorite-based products, such as chlorhexidine solutions or iodine-based preparations, are highly effective in killing MRSA bacteria. These topical products can be applied directly to the infected areas and provide localized treatment without contributing to antibiotic resistance.
“Topical therapy with sodium hypochlorite-based products is a safe and effective option for treating MRSA infections in horses. It not only kills the bacteria but also helps in wound healing and reduces the risk of resistant strains.”
Active Infection Treatment and Hygiene Practices
Proper treatment of MRSA infections in horses includes diligently managing the infection until it is fully resolved. This involves thorough cleaning and disinfection of the affected areas, applying topical therapy as recommended by a veterinarian, and monitoring the horse for signs of improvement or recurrence.
Furthermore, practicing good hygiene and implementing strict biosecurity measures are crucial to prevent the spread of MRSA among horses. This includes regularly disinfecting shared equipment, maintaining proper stable hygiene, and promoting good overall horse health and hygiene practices.
Comparison of Treatment Approaches for MRSA in Horses
| Treatment Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Systemic Antibiotics | Used in severe cases when MRSA infection is widespread or affecting deep tissues. |
| Topical Therapy | Highly effective in treating MRSA infections in horses, killing bacteria without contributing to antibiotic resistance. |
| Active Infection Management | Monitor and manage the infection until it is fully resolved, practicing good hygiene and implementing biosecurity measures to prevent spread. |
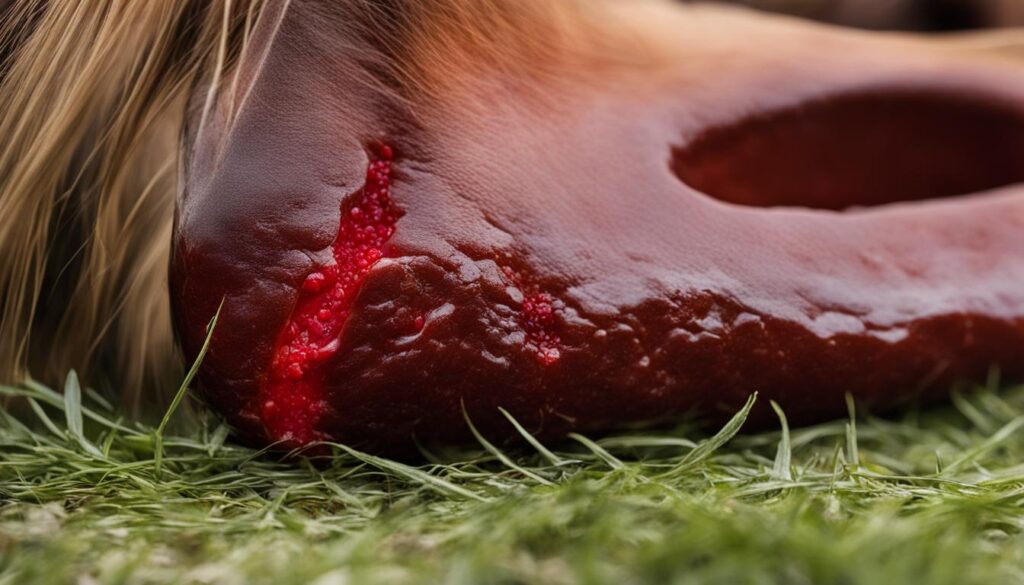
Zoonotic Potential and Human Exposure to MRSA from Horses
MRSA is not only a concern for horses but also poses a zoonotic risk, potentially infecting humans who come into contact with infected animals. Equine veterinarians and individuals who own or work with horses are at a higher risk of MRSA colonization compared to the general population.
Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial in minimizing the risk of transmission between horses and humans. One of the most effective preventive measures is proper handwashing. By washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling horses or being in their environment, you can reduce the likelihood of MRSA transmission.
“Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial in minimizing the risk of transmission between horses and humans.”
It’s essential to be aware of the symptoms of MRSA in horses and take appropriate precautions if you suspect your horse may be infected. Avoiding close contact with infected horses and their bodily fluids can significantly reduce the risk of acquiring MRSA.
Equine professionals should also recognize the importance of personal protective equipment (PPE) when dealing with potentially infected horses. Wearing gloves, masks, and gowns can provide an additional barrier against MRSA transmission.
Tips for Preventing MRSA Transmission from Horses to Humans
- Practice proper hand hygiene, including thorough handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoid close contact with infected horses and their bodily fluids.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment when handling potentially infected horses.
- Follow good biosecurity measures, such as disinfecting equipment and maintaining a clean environment for horses.
- Stay informed about MRSA and its prevention strategies by consulting reputable veterinary sources.
By taking these preventive measures, horse owners and equine professionals can significantly minimize the risk of MRSA transmission between horses and humans. Together, we can ensure the health and well-being of both our equine friends and ourselves.
Prevention Strategies for MRSA in Horses
Preventing MRSA in horses is essential to ensure their health and well-being. By implementing effective biosecurity measures and good horse hygiene practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of MRSA transmission. Here are some key prevention strategies:
- Routine Handwashing: Wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling horses, especially if you have been in contact with multiple horses or have touched potential sources of infection.
- Minimize Grooming Contact: Avoid sharing grooming equipment between horses, especially if they are new or transient horses. Use individual brushes, combs, and other grooming tools for each horse to prevent the spread of MRSA.
- Use Sodium Hypochlorite Topical Products: Incorporate sodium hypochlorite-based products into your routine horse hygiene practices. These products are effective in killing MRSA bacteria and preventing infections.
- Minimize Horse-to-Horse Contact: Limit close contact between horses, especially if an infection is present. This can help prevent the spread of MRSA and other infectious diseases.
- Practice Good Biosecurity Measures: Implement strict biosecurity protocols on your premises, such as regular cleaning and disinfection of horse stalls and equipment. This can help minimize the risk of bacterial contamination and transmission.
By following these prevention strategies, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of MRSA infections in horses, promoting their overall health and well-being.
| Prevention Strategies for MRSA in Horses | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Routine Handwashing | – Reduces the risk of MRSA transmission – Promotes personal hygiene |
| Minimize Grooming Contact | – Prevents the spread of MRSA between horses – Limits the risk of infection |
| Use Sodium Hypochlorite Topical Products | – Effectively kills MRSA bacteria – Provides an additional layer of protection |
| Minimize Horse-to-Horse Contact | – Reduces the chance of MRSA transmission – Minimizes the spread of other infectious diseases |
| Practice Good Biosecurity Measures | – Limits bacterial contamination – Protects the overall horse population |
Conclusion
MRSA, a multi-drug resistant bacteria, poses a significant threat to horse health and is challenging to treat due to its resistance to common antibiotics. Preventing MRSA in horses requires a proactive approach, focusing on routine hygiene practices and effective biosecurity measures. By implementing preventive strategies such as proper hand hygiene, minimizing contact with infected horses, and using individual equipment and topical therapies, horse owners can play a crucial role in protecting their beloved equines.
Understanding the transmission routes of MRSA and its potential to cause zoonotic diseases in humans is vital. Equine professionals and individuals in close contact with horses, particularly those with MRSA infections, are at a higher risk of contracting the bacteria. By prioritizing good hygiene practices, such as thorough handwashing and maintaining a clean environment, the risk of MRSA transmission between horses and humans can be minimized.
Preventing MRSA in horses not only safeguards their health but also reduces the risk of spreading the bacteria to other animals. By staying vigilant and implementing preventive measures, horse owners can contribute to the overall well-being of the equine community. By understanding the importance of MRSA prevention and taking proactive steps, we can effectively protect the health of our horses and minimize the risk of zoonotic diseases.
FAQ
What is MRSA and how does it impact horses?
MRSA stands for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a multi-drug resistant form of bacteria that can cause infections in horses. It can lead to skin and soft tissue infections, as well as more severe infections in joints and deep tissue.
How prevalent is MRSA in horses and what are the risk factors?
MRSA is becoming more common in horses and has been established as an endemic pathogen in many horse populations. Risk factors for MRSA in horses include undergoing surgeries, repeated exposure to antibiotics, close contact with infected horses, shared grooming equipment, and poor hygiene practices.
How is MRSA in horses diagnosed?
MRSA in horses is diagnosed through a skin swab or tissue sample, which is cultured in a laboratory. The bacterial growth is identified, and an antibiotic sensitivity panel is performed to determine the appropriate antibiotic choice.
How is MRSA in horses treated and managed?
The treatment of MRSA in horses involves a combination of systemic and topical therapy. Severe cases may require systemic antibiotics, but the choices are often limited due to antibiotic resistance. Topical therapy, such as sodium hypochlorite-based products, is highly effective in treating MRSA infections in horses.
Can MRSA in horses be transmitted to humans?
Yes, MRSA can be transmitted from horses to humans, leading to zoonotic infections. Equine veterinarians and individuals who own or work with horses have a higher incidence of MRSA colonization compared to the general population.
How can MRSA in horses be prevented?
Preventing MRSA in horses involves implementing effective biosecurity measures and good horse hygiene practices. This includes routine handwashing, minimizing contact with infected horses, using individual equipment for each horse, and practicing good biosecurity measures to reduce the risk of transmission.
Is MRSA a growing concern in horse health?
MRSA is indeed a growing concern in horse health due to its resistance to common antibiotics. Understanding MRSA and implementing prevention strategies are crucial to protecting horses and minimizing the risk of transmission to humans and other animals.


